Abstract
Background: Concizumab is an anti-tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) antibody under development as a once-daily subcutaneous prophylactic treatment for patients with hemophilia with and without inhibitors. Results from the main part of the phase 3 explorer7 trial (NCT04083781) are presented by hemophilia subtype for patients with inhibitors (hemophilia A or B with inhibitors [HAwI or HBwI]).
Aims: To assess efficacy and safety of daily concizumab prophylaxis versus no prophylaxis by hemophilia subtype (patients with HAwI or HBwI).
Methods: Patients in explorer7 were randomized 1:2 to no prophylaxis (arm 1; ≥24 weeks) or concizumab prophylaxis (arm 2; ≥32 weeks), or assigned to concizumab prophylaxis (arms 3 & 4). Randomization was stratified according to hemophilia type and bleeding frequency prior to screening. After the main part, all patients were offered entry into the extension part, and patients in arm 1 would then switch to concizumab treatment. After treatment restart following the treatment pause due to thromboembolic events, patients received a 1.0 mg/kg concizumab loading dose on Day 1, followed by an initial 0.20 mg/kg daily dose starting Day 2, with potential adjustment to 0.15 or 0.25 mg/kg based on measured plasma concizumab concentration level after week 4. The exploratory analysis presented here evaluates concizumab efficacy and safety by hemophilia subtype, with results presented separately for HAwI and HBwI after the treatment pause. The study was not powered to assess differences by hemophilia subtype (the primary analysis was conducted with HAwI and HBwI combined). Annualized bleeding rate (ABR) was estimated using a negative binomial regression model, with the logarithm of the length of the observation period as offset, and treatment and bleeding frequency prior to screening as factors. Patients were asked at each visit whether they experienced any adverse events (AEs) since the last visit, and all AEs observed by the investigator or reported by the patient were recorded and evaluated. Informed consent and ethics committee approval were obtained.
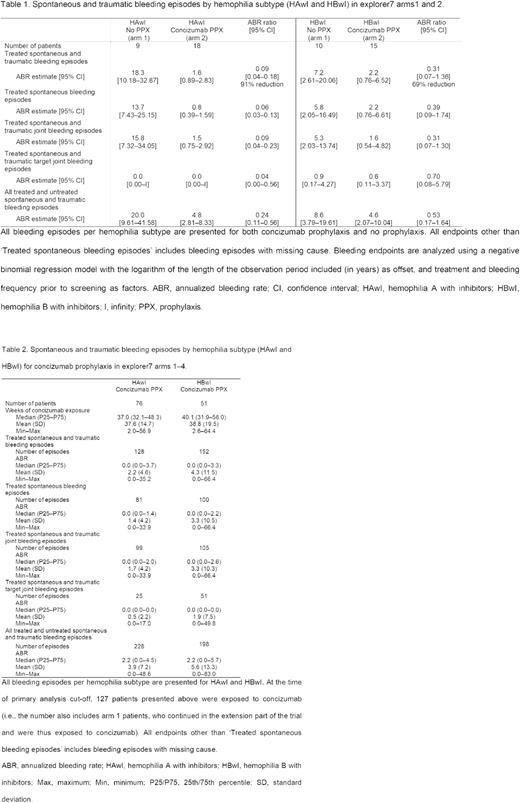
Results: Of 133 patients in the trial, 52 patients were randomized to concizumab prophylaxis (arm 2: HAwI, n=18; HBwI, n=15) or no prophylaxis (arm 1: HAwI, n=9; HBwI, n=10). The remaining 81 patients were assigned to concizumab prophylaxis (non-randomized arms 3 & 4). Estimated mean ABRs for both hemophilia subtypes are presented in Table 1. The estimated mean ABR for treated spontaneous and traumatic bleeding episodes in patients with HAwI was 1.6 (95% CI, 0.9-2.8) for concizumab prophylaxis versus 18.3 (95% CI, 10.2-32.9) for no prophylaxis (ABR ratio, 0.09 [95% CI, 0.04-0.18]). The estimated mean ABR in patients with HBwI was 2.2 (95% CI, 0.8-6.5) for concizumab prophylaxis versus 7.2 (95% CI, 2.6-20.1) for no prophylaxis (ABR ratio, 0.31 [95% CI, 0.07-1.36]). The overall median ABR on concizumab prophylaxis was 0.0 in both the HAwI and HBwI subgroups (arms 1 to 4). Median ABRs for both hemophilia subtypes are presented in Table 2. Following the treatment restart, no thromboembolic events were reported while on concizumab treatment in patients with either HAwI or HBwI.
Conclusions: Once-daily, subcutaneous concizumab prophylaxis was effective in reducing ABR versus no prophylaxis in patients with either HAwI or HBwI. The overall median ABR was 0.0 across both hemophilia subtypes. Concizumab was considered safe and well tolerated in patients with HAwI and HBwI with no thromboembolic events reported after treatment restart.
Disclosures
Cepo:Novo Nordisk: Current Employment, Current equity holder in private company. d'Oiron:Spark Therapeutics: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Pfizer: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Octapharma: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Biomarin: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Baxalta/Shire/Takeda: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; CSL Behring: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; LFB: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Novo Nordisk: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Sobi: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Roche: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Mathias:Freeline 2019: Consultancy; Novo Nordisk: Research Funding; Sanofi: Research Funding; Roche: Research Funding; Sobi: Research Funding; Octapharma: Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. Odgaard-Jensen:Novo Nordisk: Current Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal